A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Click a letter to see a list of medical procedures beginning with that letter.
Click 'Back to Intro' to return to the beginning of this section.
Having a Contrast Echocardiogram
Your health care provider recommends that you have a contrast echocardiogram (also called a contrast echo). This is an imaging test that uses sound waves (ultrasound) to take pictures of the heart while it's beating. During the test, a special dye (contrast agent) is injected into your vein to help show structures in the heart with more detail. It allows the inside of the heart to be seen more clearly on the ultrasound pictures. A contrast echo is most often done when standard echocardiogram images are not of good enough quality to see all the details of the heart. From start to finish, the test takes about 30 minutes. An echocardiogram lets your provider see how well the heart muscle is working, check the size of the heart chambers, and see how the valves are functioning.
Before the test
-
Follow any instructions given by your health care provider to prepare for the test.
-
You may be asked not to eat a heavy meal before the test to improve the images of the heart.
-
On the day of the test, wear a two-piece outfit. You may need to undress from the waist up and put on a hospital gown.
Let the technologist know
For your safety, let the technologist know if you:
-
Have a known or suspected heart or lung problem.
-
Have any other medical conditions.
-
Are allergic to perflutren (contrast agent), blood, blood products, albumin, or any medicines.
-
Are taking any medicines, including vitamins, herbs, and over-the-counter medicines.
-
Are or may be pregnant.
-
Are breastfeeding.
During the test
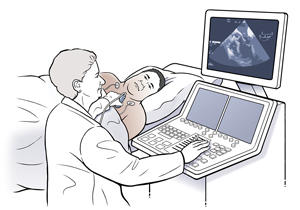
A contrast echo is done by an ultrasound technologist (sonographer). A nurse or another health care provider (cardiologist) may also be present during the test.
-
You’ll lie on your back on an exam table or hospital bed.
-
An I.V. line is placed into a vein in your arm or hand.
-
Small pads (electrodes) are placed on your chest to monitor your heart rate. Special equipment is used to monitor your vital signs (blood pressure, breathing, and blood oxygen level).
-
A cool, clear, or blue-colored gel is placed on your chest. Then a handheld device called a transducer is moved firmly over your chest. The transducer releases harmless sound waves. These are processed by a computer. Live pictures of your heart can then be viewed on a monitor.
-
The contrast agent is injected through the I.V. line into your bloodstream to reach your heart.
-
At times, you may be asked to change positions. This allows pictures of your heart to be taken from different angles. You may also be asked to hold your breath for a few seconds. This helps prevent the pictures from being blurry.
-
When the test is complete, the gel is cleaned off your chest and the I.V. line is removed from your arm or hand.
-
The pictures of your heart are sent to your health care provider or a cardiologist for review.
After the test
-
You may need to rest after the test. Your vital signs will continue to be monitored during this time. You’ll be told when you can go home.
-
After you go home, return to your usual activities when you feel ready.
Risks and possible complications
Risks and possible complications of a contrast echo include:
-
Excessive bruising, bleeding, swelling, or other problems at the I.V. site.
-
Tenderness on the chest wall from pressing the transducer against the tissue.
-
Side effects, such as dizziness, weakness, fatigue, palpitations, headaches, and nausea.
-
An allergic reaction to the contrast (rash, hives, trouble breathing, swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue). If you have an allergic reaction to the contrast, report it immediately and call 911 for any breathing difficulties.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your health care provider, or as advised. They will go over the test results with you during a follow-up visit. This is usually within 1 to 2 weeks. Be sure to share any concerns you have with your provider.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Robyn Zercher FNP
Online Medical Reviewer:
Stacey Wojcik MBA BSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Steven Kang MD
Date Last Reviewed:
2/1/2025
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.