A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Click a letter to see a list of conditions beginning with that letter.
Click 'Topic Index' to return to the index for the current topic.
Click 'Library Index' to return to the listing of all topics.
When Your Child Has a Gastric or Duodenal Ulcer
An ulcer is a breakdown of tissue on the inside of the stomach or small intestine. This causes a sore to form. An ulcer can form in the stomach. This is called a gastric ulcer. Or one can form in the first part of the small intestine. This is called a duodenal ulcer. In children, ulcers are often caused by an infection with bacteria, such as Helicobacter pylori. Or they may be caused by certain medicines, such as NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). They may also be caused by an increase in stomach acid.
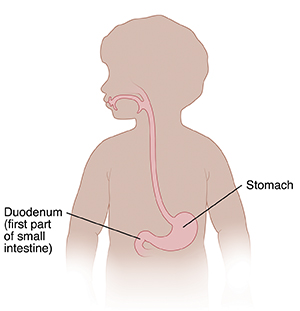
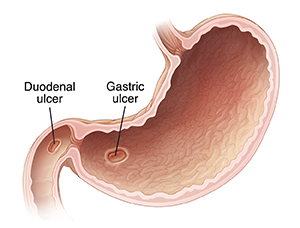 |
| The ulcer may be located anywhere in the stomach or duodenum. |
What are the symptoms of an ulcer?
Common symptoms of a gastric or duodenal ulcer include:
-
Burning feeling, cramping, or pain that feels like hunger in the belly. This often happens 1 to 3 hours after a meal, or in the middle of the night.
-
Pain that gets better or worse with eating
-
Upset stomach (nausea) or vomiting
-
Signs of blood in vomit
-
Black poop (stool) that's sticky like tar. This means the ulcer is bleeding.
How are ulcers diagnosed?
The healthcare provider will ask about your child’s symptoms. Your child may also need a test. Common tests for an ulcer include:
-
Upper GI series. This is a series of X-rays of the digestive tract.
-
Endoscopy. This test uses a thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera attached (endoscope). The endoscope is put into your child’s mouth into the stomach. This allows the healthcare provider to see the ulcer. This tube may also be used to take a tiny tissue sample (biopsy).
-
Blood, breath, or stool tests. These can help show an infection that can cause an ulcer.
How are ulcers treated?
Ulcers in children are most often treated with medicine. The most common medicines are H-2 blockers and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). They help by preventing acid from being made in the stomach. It may take 8 to 12 weeks of medicine to relieve your child’s symptoms and heal the ulcer.
Long-term concerns
A child who has had an ulcer is more likely to have one again. Watch your child for ulcer symptoms. If your child has any symptoms, contact their healthcare provider right away. If an ulcer isn't treated, a serious problem called perforation can occur. This is a hole through the stomach or intestinal wall. Emergency surgery will likely be needed to fix a perforation. Untreated ulcers can also cause unintended weight loss and ongoing belly (abdominal) pain. A bleeding ulcer can also cause low levels of red blood cells in the blood (anemia).
When to call the healthcare provider
Call your child’s healthcare provider right away if you see signs that your child’s ulcer is worse or perforated. Watch for:
-
Fever
-
Blood in the vomit
-
Severe belly pain
Online Medical Reviewer:
Amy Finke RN BSN
Online Medical Reviewer:
L Renee Watson MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Liora C Adler MD
Date Last Reviewed:
6/1/2022
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.